Migraines: Like an Ice Pick to the Brain
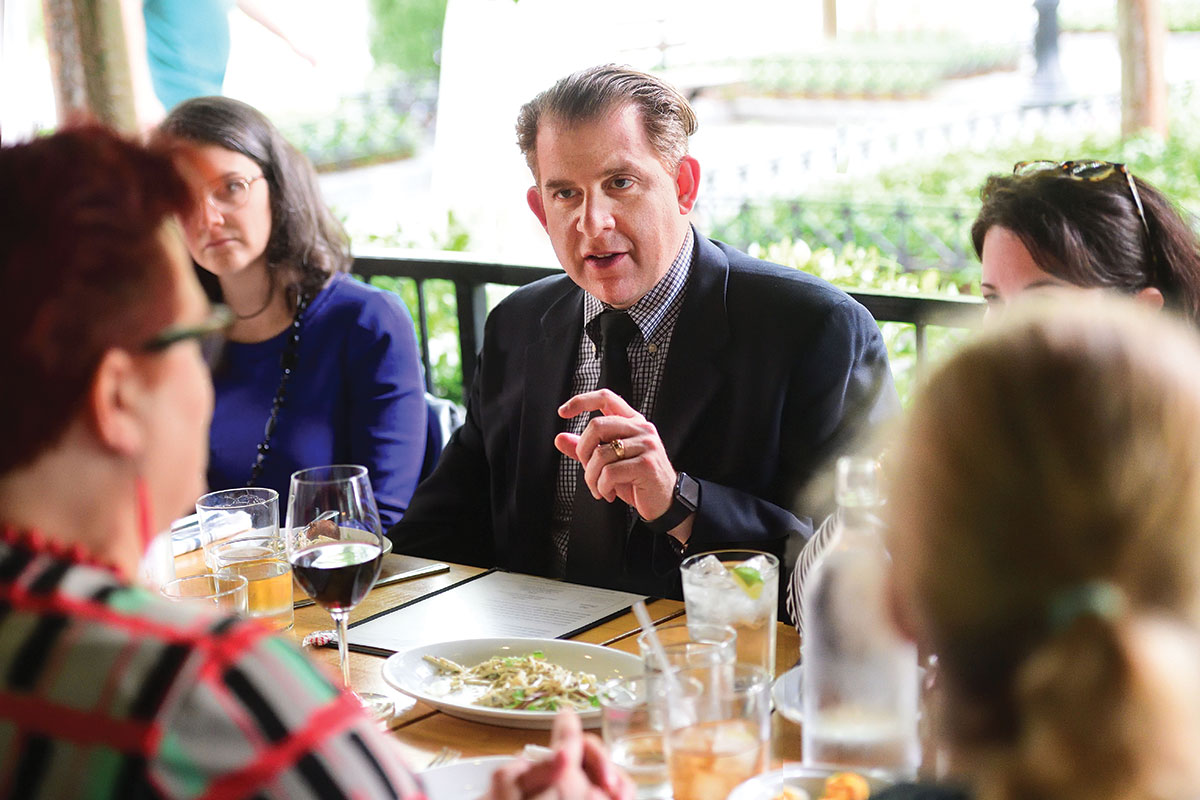

A migraine is not "just a headache," say migraine sufferers, a group of whom met for dinner with Emory neurologist Gregory Esper. For this "dinner with a doctor" get together, guests discussed migraine symptoms, treatments, and medications, and how these severe headaches have impacted their lives."
A breeze drifts across the restaurant patio, where diners are clustered around long tables in bright green chairs that match the park-like setting. As the group looks over the dinner menu, neurologist Gregory Esper cautions everyone to make their selections carefully.
“There are foods and drinks that can induce migraines,” says Esper, director of general neurology and neuromuscular diseases at Emory Clinic and associate professor at Emory School of Medicine. “The most common are processed meats, aged cheeses, and red wine. But you might be sensitive to a particular food not on the ‘list.’ I know one woman who would get a migraine if she had the artificial sweetener stevia. Aspartame in diet drinks can be a trigger as well.”
Beyond migraines being a clinical interest, Esper himself suffers from them, as do each of the five guests. This is an opportunity to discuss migraine symptoms, triggers, treatments, and medications with an expert over a casual dinner. While Esper can’t offer specific suggestions in this situation, he can discuss generalities and answer questions broadly. “So, what constitutes a migraine as opposed to a headache?” Esper asks. “Well, it should be throbbing in nature, at least moderately intense, and usually only on one side. In fact, the word is French for ‘pain in one half of the head.’ ”

Migraines can last from hours to days—most last 4 to 72 hours without treatment—and are sporadic. “If someone has a headache every day, that signals that it is not just a migraine,” says Esper. “Something else is going on.” In about 10 percent of cases of migraine-like headaches, the root cause is something else—a secondary condition.
The majority of migraine sufferers—60 percent to 80 percent—experience “common migraines,” in which the main symptom is the pain itself. “Classical migraines,” which include auras or other visual or sensory changes, can feel dangerous but usually are not, says Esper. “You might wonder if you’re having a stroke,” he says, “but a stroke is associated with a headache in only about 8 percent of cases.”
The thinking is that, due to a stimulus and genetics, deep structures in the brain trigger activation of the “trigeminovascular system.” This causes blood vessels to dilate along the covering of the brain—the meninges—which is a very sensitive structure. Inflammatory mediators and neurotransmitters then seep onto the surface of the meninges, further dilating blood vessels and making them more “leaky.” These mediators and neurotransmitters excite the trigeminal nerve—the largest and most complex of the cranial nerves, responsible for sensation in the face and head—which stimulates the meninges to send signals to the part of the brain that senses pain.
“It becomes a vicious cycle,” Esper says, “which is why the pain can last a long time unless we cut it off with medications.”

When migraines start at a young age and are not treated correctly, they can change brain physiology. For some, migraines start at puberty and peak in middle age.
Others have experienced migraines since early childhood. For still others, migraines come on later in life, or after an event or injury.
One participant says his first migraine occurred after he fell in the night due to a spell of vertigo, and that he experienced a visual shift as well.
Sometimes, the participants say, they see flashing lights or feel strange before the headache’s onset—numb, tingly, or overly sensitive to stimuli.
“I don’t see auras, but sometimes I smell roses,” says one.
“Are there migraine-sniffing animals?” asks another. “My dog will come up to me and smell my eyeball and within an hour or two, I’ll have a migraine.”
“I don’t know about that,” says Esper, smiling, “but visual or sensory changes, and nausea or
Most migraines involve a pulsing type of pain, which can migrate, says Esper. “Mine
“Mine feel like there’s an ice pick in my head,” says one participant. “Pain was just something I thought was normal.”
Preventing a migraine is far superior to trying to get rid of one that is
“In the past 10 years, I have had tension-type headaches that, if controlled quickly with Fioricet, will go away,” says a participant who has had lifelong migraines. “If not, they will morph into a migraine in less than an hour.”
In general, Esper says, migraine pain is caused by vasodilation (expansion) in the cranial blood vessels, while headache pain is caused by vasoconstriction (narrowing) of the blood vessels.
Therefore, migraine medications are largely vasoconstrictors: first the ergots and then, in the 1990s, triptans, which are serotonin receptor agonists.
Most at the table have tried a host of medications—Imitrex injections and pills, Treximet, Relpax, Maxalt, Zomig, Amerge, Fioricet. Triptans with naproxen sodium. Dilaudid with Phenergan injections (for migraines severe enough for an ER visit.)

“I take topiramate (Topomax) daily, which is designed to prevent migraines, and in the three years since I’ve been taking it, the number of migraines I have and their severity has gone down considerably,” says one participant. “I also take rizatriptan, a triptan that I call ‘the magic pill.’ It stops the bad feedback loop that leads to a migraine.”
Participants agree that taking medicine too late is useless. “I’m trying to learn not to be stingy with my pills and to take one when I feel the first symptoms, whether a light headache, or nausea, or an aura,” says one. “I keep up with my refills so I never feel like I’m going to run out.”
Several of the participants say they treat their migraines with Botox. “It’s like I’m getting away with something,” says one. “The first time I didn’t have a headache after Botox, I couldn’t believe it. It’s 37 injections all over my head. I go every 90 days for injections, and I’m mostly free of migraines for the first time in my life. I didn’t know people were living like this, without pain.”
Esper makes a point to ask patients what is going on in their lives—relationships, work, diet, travel—since migraines can have environmental triggers. “An accountant comes to me every March to get ready for tax season,” Esper says. “Stress and sleepless nights can bring migraines on.”
One participant’s migraines had been misdiagnosed for 11 years as sinus headaches. Another went on vacation for 10 days and didn’t have one the entire time—she wasn’t sure if it was due to change of climate or less stress.
Estrogen, through hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives, can help or hurt, says Esper.
Some antidepressants are used to treat migraines—Esper recommends tricyclic antidepressants as first-line therapies. Other antidepressant drug classes may not work as well. “Cymbalta—it’s like putting my brain in a sling,” says one participant. “My knitting gets looser. I’m more relaxed.”
A “what if” question is posed: What if you had never had migraines? Some participants say they might have taken part in more activities, been more social, worried less.
Esper, who first experienced migraines in medical school and residency when he was under pressure and getting little sleep, says his migraines have one upside: “They have given me more empathy and compassion for my patients.”
Dinner with a Doctor Participants
Wendy Darling
Communications Specialist
First migraine at 11 or 12
Usual symptoms: Pain on one side of face, often at temple or eye socket, like a spike through my head or a rock pressing against it, pain in the back, lower neck, nausea, feeling “floaty” or dizzy, hard time focusing.
What helps: Topiramate and Rizatripan, and hot showers with water directed at my face and head.

Andrew Thompson
lawyer
First migraine about 6
Usual symptoms: Often begins with a pulsing headache on one side of forehead, usually the right, with pain and behind right eye. The migraine will spread from the forehead to the base of the skull, close to the neck, on the same side. “The migration may take a day or two until I eventually become very sensitive to light."
What helps: Lots of sleep, eliminating dark chocolate, wine, and other foods and beverages with tannins from my diet. As far as medicines, Excedrin migraine and sometimes an Imitrex when one is at its worst.

Claire Hennessey
fundraising director
First migraine at 13
Usual symptoms: Intense pain at base of neck and behind left eye, nauseous, very sensitive to smell and light, unable to focus.
What helps: ”I have tried every Triptan in the book, nerve blocks, Eastern and Western medicine—what’s working for me now is the use of two preventive daily medications, Botox injections every three months, and Imitrex when I get a migraine.”

Susan Scarbrough
executive assistant/editor
First migraine: "I have never not had migraines."
Usual symptoms: In the last decade, pain either unilateral (right frontal) or bilateral. Sometimes I feel like my right ear needs to pop.
What helps: Imitrex injections, Imitrex pills, Treximet, Relpax pills and dissolvables, Maxalt pills and dissolvables, Zomig dissolvables, Amerge pills, Fioricet. Triptans always perform better for me in combination with naproxen sodium. In the ER, Dilaudid with Phenergan piggyback injections.

John Johnston
English professor
First migraine: adult
Usual symptoms: Visual shift in perception, pain.
What helps: Relaxing, being in a dark room, medications.

Windows of Opportunity
You can support efforts of more than 400 Emory brain health researchers and clinicians to transform how we predict, prevent, treat, and cure brain disorders and diseases.
To find out more, contact Courtney Harris, director of development, at 404-727-5282 or courtney.harris@emory.edu