Civil War plant
medicines blast drug-resistant bacteria
Emory lab explores remedies in 1863 guide for battlefield surgeons

During the height of the Civil War, the Confederate Surgeon General commissioned a guide to traditional plant remedies of the South, as battlefield physicians faced high rates of infections among the wounded and shortages of conventional medicines. A new study of three of the plants from this guide — the white oak, the tulip poplar and the devil’s walking stick — finds that they have antiseptic properties.
Scientific Reports published the results of the study led by scientists at Emory University. The results show that extracts from the plants have antimicrobial activity against one or more of a trio of dangerous species of multi-drug-resistant bacteria associated with wound infections: Acinetobacter baumannii, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae.

Francis Porcher, a botanist and surgeon from South Carolina, compiled "Resources of the Southern Fields and Forests," which included plant remedies used by Native Americans and enslaved Africans. This 1863 copy is from Emory’s Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives and Rare Book Library.
Francis Porcher, a botanist and surgeon from South Carolina, compiled "Resources of the Southern Fields and Forests," which included plant remedies used by Native Americans and enslaved Africans. This 1863 copy is from Emory’s Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives and Rare Book Library.
“Our findings suggest that the use of these topical therapies may have saved some limbs, and maybe even lives, during the Civil War,” says Cassandra Quave, senior author of the paper and assistant professor at Emory’s Center for the Study of Human Health and the School of Medicine’s Department of Dermatology.
Quave is an ethnobotanist, studying how people use plants in traditional healing practices, to uncover promising candidates for new drugs. “Ethnobotany is essentially the science of survival — how people get by when limited to what’s available in their immediate environment,” she says. “The Civil War guide to plant remedies is a great example of that.”
“Our research might one day benefit modern wound care, if we can identify which compounds are responsible for the antimicrobial activity,” says Micah Dettweiler, the first author of the paper.
If the active ingredients are identified, “it is my hope that we can then [further] test these molecules in our world-renowned models of bacterial infection,” says co-author Daniel Zurawski, chief of pathogenesis and virulence for the Wound Infections Department at the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research.
“I’ve always been a Civil War buff,” Zurawski adds. “I am also a firm believer in learning everything we can garner from the past so we can benefit now from the knowledge and wisdom of our ancestors.”
Additional co-authors on the paper include Ryan Reddinger, from the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research; James Lyles, from the Quave lab; and Kate Nelson, from Emory School of Medicine’s Department of Dermatology.


Dettweiler was still an Emory undergraduate when he heard about the Civil War plant guide and decided to research it for his honors thesis. He has since graduated with a degree in biology and now works as a research specialist in the Quave lab.
“I was surprised to learn that far more Civil War soldiers died from disease than in battle,” he says. “I was also surprised at how common amputation was as a medical treatment for an infected wound.”
About one in 13 surviving Civil War soldiers went home with one or more missing limbs, according to the American Battlefield Trust.
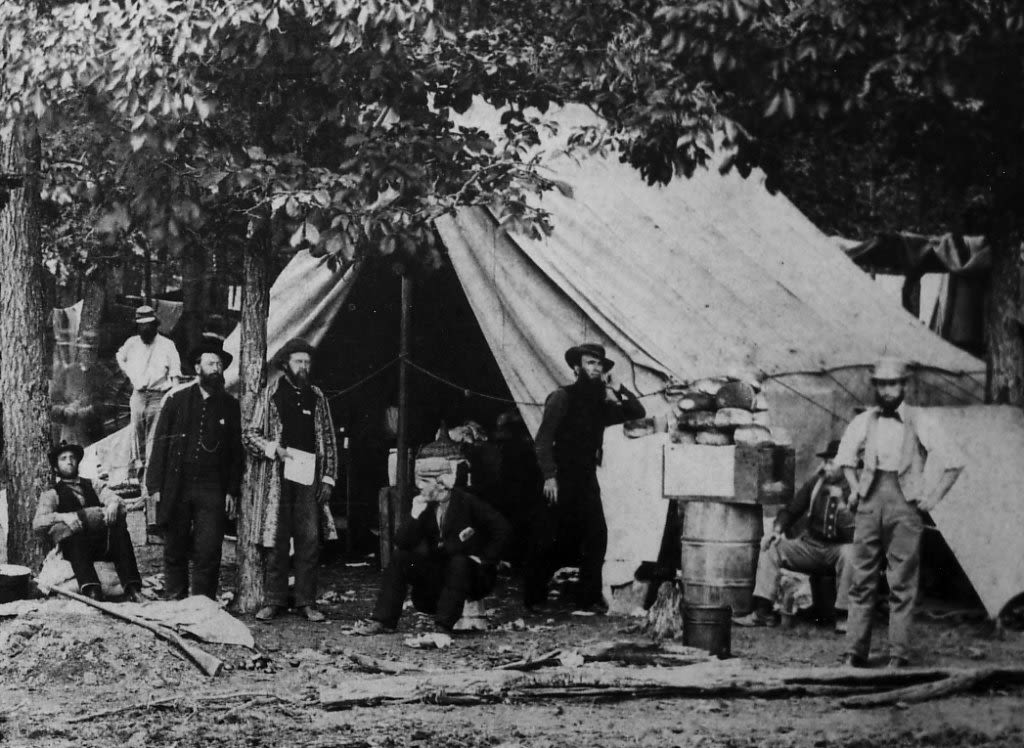

A field hospital at Gettysburg. (National Park Service)
A field hospital at Gettysburg. (National Park Service)
At the time of the Civil War, from 1861 to 1865, germ theory was in its developmental stages and only gradually beginning to gain acceptance. Formal medical training for physicians was also in its infancy. An antiseptic was simply defined as a tonic used to prevent “mortification of the flesh.” Iodine and bromine were sometimes used to treat infections, according to the National Museum of Civil War Medicine, although the reason for their effectiveness was unknown.

A cartoon map, created in 1861, uses a snake to illustrate Gen. Winfield Scott’s plan to crush the Confederacy economically through a blockade, sometimes called the “Anaconda plan.” (Library of Congress)
A cartoon map, created in 1861, uses a snake to illustrate Gen. Winfield Scott’s plan to crush the Confederacy economically through a blockade, sometimes called the “Anaconda plan.” (Library of Congress)
Other conventional medicines available at the time included quinine, for treating malaria, and morphine and chloroform, to block pain.
Military field hospitals within the Confederacy, however, did not have reliable access to these medicines due to a blockade — the Union Navy closely monitored the major ports of the South to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
Seeking alternatives, the Confederacy commissioned Francis Porcher, a botanist and surgeon from South Carolina, to compile a book of medicinal plants of the Southern states, including plant remedies used by Native Americans and enslaved Africans. “Resources of the Southern Fields and Forests,” published in 1863, was a major compendium of uses for different plants, including a description of 37 species for treating gangrene and other infections. Samuel Moore, the Confederate Surgeon General, drew from Porcher’s work to produce a document called “Standard supply table of the indigenous remedies for field service and the sick in general hospitals.”
“Plants have a great wealth of chemical diversity, which is one more reason to protect natural environments."
Micah Dettweiler
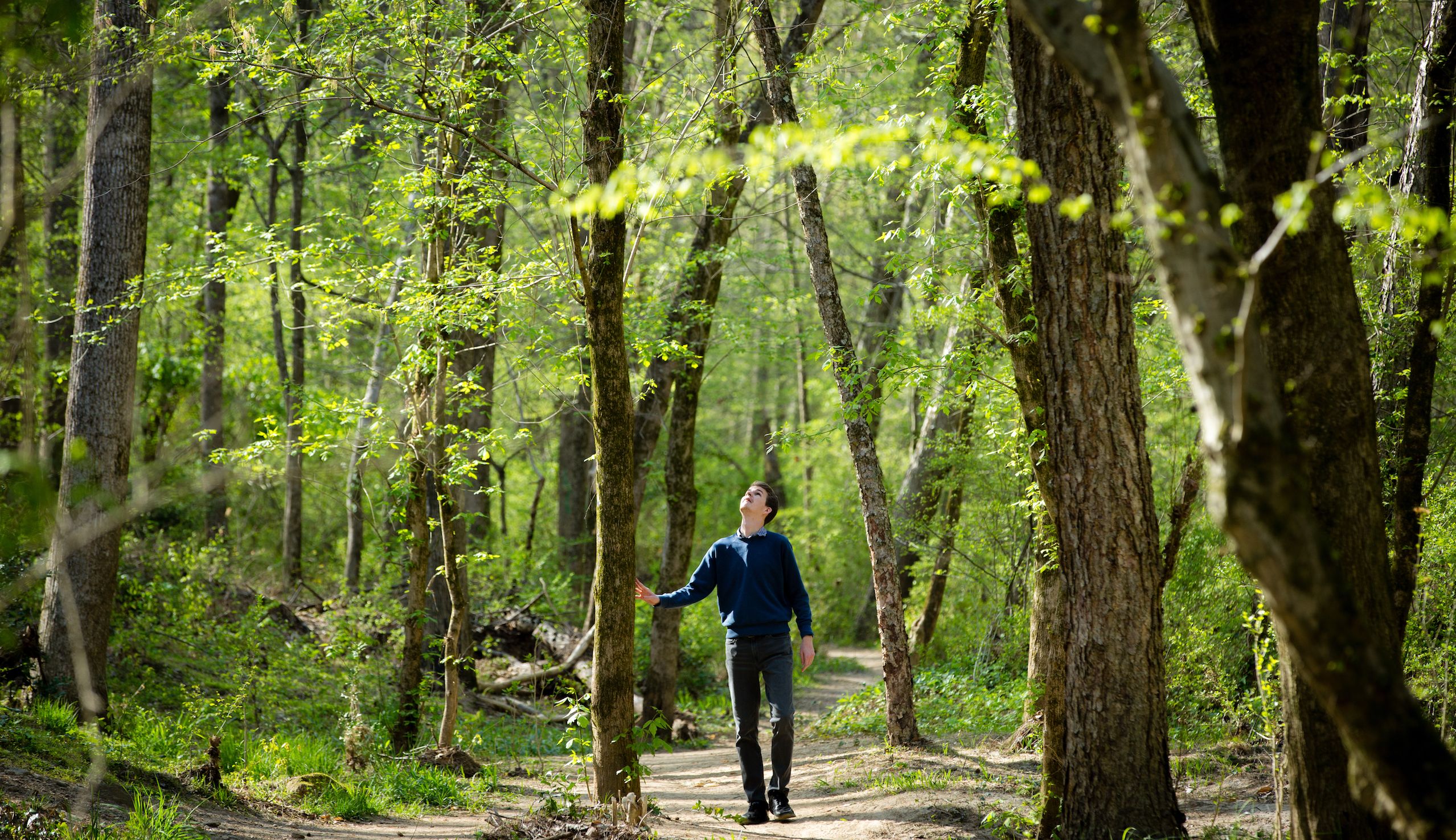

For the current study, the researchers focused on three plant species Porcher cited for antiseptic use that grow in Lullwater Preserve on the Emory campus. They included two common hardwood trees — the white oak (Quercus alba) and the tulip poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera) — as well as a thorny, woody shrub commonly known as the devil’s walking stick (Aralia spinosa).
Samples of these three plants were gathered from campus specimens, based on Porcher’s specifications. Extracts were taken from white oak bark and galls; tulip poplar leaves, root inner bark and branch bark; and the devil’s walking stick leaves. The extracts were then tested on three species of multi-drug-resistant bacteria commonly found in wound infections.
Aceinetobacter baumannii — better known as “Iraqibacter” due to its association with wounded combat troops returning from the Iraq War — exhibits extensive resistance to most first-line antibiotics. “It’s emerging as a major threat for soldiers recovering from battle wounds and for hospitals in general,” Quave says.
Staphylococcus aureus is considered the most dangerous of many common staph bacteria and can spread from skin infections or medical devices through the bloodstream and infect distant organs. Klebsiella pneumoniae is another leading cause of hospital infection and can result in life-threatening cases of pneumonia and septic shock.
Culturing bacteria for an experiment in the lab.
Culturing bacteria for an experiment in the lab.
Laboratory tests showed that extracts from the white oak and tulip poplar inhibited the growth of S. aureus, while the white oak extracts also inhibited the growth of A. baumannii and K. pneumoniae. Extracts from both of these plants also inhibited S. aureus from forming biofilms, which can act like a shield against antibiotics.
Extracts from the devil’s walking stick inhibited both biofilm formation and quorum sensing in S. aureus. Quorum sensing is a signaling system that staph bacteria use to manufacture toxins and ramp up virulence. Blocking this system essentially “disarms” the bacteria.
"Our findings suggest these topical therapies may have saved some limbs during the Civil War.”
Cassandra Quave
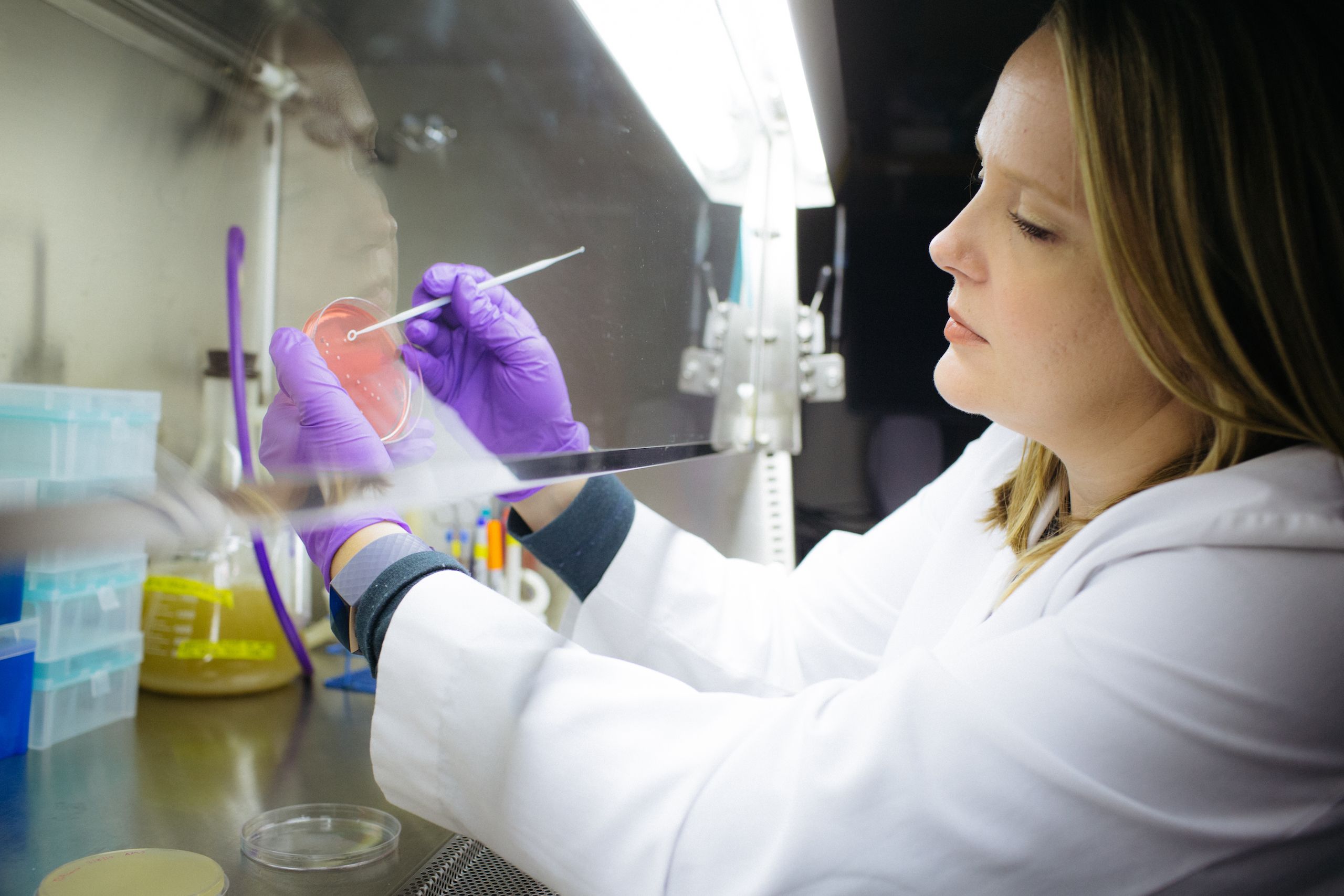

Traditional plant remedies are often dismissed if they don’t actively attack and kill pathogens, Quave notes, adding: “There are many more ways to help cure infections, and we need to focus on them in the era of drug-resistant bacteria.”
“Plants have a great wealth of chemical diversity, which is one more reason to protect natural environments,” Dettweiler says. He plans to go to graduate school with a focus on researching plants for either medical or agricultural purposes. “I’m interested in plants because, even though they don’t move from place to place, they are extremely powerful and important.”
The research was supported by a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Science Education Program award to Emory University and grants from the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health and from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease.

To learn more, please visit:
The Quave Research Group, the Emory Center for the Study of Human Health, the Emory School of Medicine Department of Dermatology, Emory Antibiotic Resistance Center, Emory University Herbarium, the Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives and Rare Book Library